Secondary metabolites, also known as phytochemicals, represent a large subset of plant molecules that include compounds with health-promoting effects. Indeed, a number of epidemiological studies have shown that, when taken regularly and in adequate amounts, these molecules can have long-term beneficial effects on human health, through reduction of the incidence of degenerative diseases, such as cardiovascular diseases, obesity, diabetes, and cancer. As the dietary intake of these phytochemicals is often inadequate, various strategies are in use to improve their content in staple crops, and the end-products thereof. One of the most effective strategies is crop improvement through genetic approaches, as this is the only way to generate new cultivars in which the high accumulation of a given phytochemical is stably fixed. Efforts to genetically improve quality traits are rapidly evolving, from classical breeding to molecular-assisted approaches; these require sound understanding of the molecular bases underlying the traits, to identify the genes/alleles that control them. This can be achieved through global analysis of the metabolic pathway responsible for phytochemical accumulation, to identify the link between phytochemical content and the activities of key enzymes that regulate the metabolic pathway, and between the key enzymes and their encoding genes/alleles. Once these have been identified, they can be used as markers for selection of new improved genotypes through biotechnological approaches. This review provides an overview of the major health-promoting properties shown to be associated with the dietary intake of phytochemicals, and describes how molecular approaches provide means for improving the health quality of edible crops. Finally, a case study is illustrated, of the identification in durum wheat of the Lipoxygenase-B1 genes that control the final carotenoid content in semolina-based foods, such as pasta products.
Figure 1. Schematic representation of the biosynthesis of secondary metabolites. E4P, erythrose 4-phosphate; G3P, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate; PEP, phosphoenolpyruvate; PYR, pyruvate; DOX5P, deoxyxylulose 5-phosphate; IPP, isopentenyl pyrophosphate; DMAPP, dimethylallyl pyrophosphate; PP, pyrophosphate; GPP, geranyl pyrophosphate; FPP, farnesyl pyrophosphate; GGPP, geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate.
Figure 5. Outline of how a functional approach can contribute to identification of a candidate gene associated with high levels of a health-promoting phytochemical in a staple crop. A germplasm collection is screened to determine the variability in nature of the trait. Genotypes characterized by contrasting metabolite accumulation are subjected to enzymatic analysis to identify key enzyme variants (i.e., allozymes) that are characterized by contrasting activities/efficiencies, and molecular analysis to identify alleles that encode the different allozymes and to evaluate their expression levels.
Then, on the basis of both the enzymatic and molecular information, a candidate gene/allele can be identified that can then be efficiently used in advanced breeding programs that are aimed at the introgression of the trait of interest into an elite cultivar.
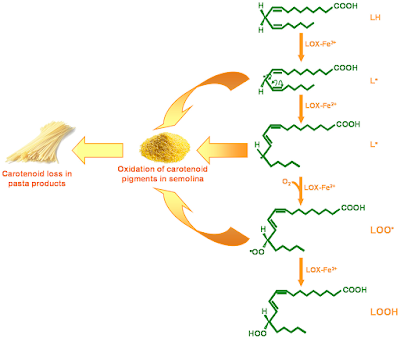
Figure 6. Reaction catalyzed by lipoxygenase (LOX) during pasta processing. LOX catalyzes hydroperoxidation of free linoleate (LH), to give the corresponding hydroperoxide (LOOH). pasta processing the pentadienyl (L°) and peroxy radicals (LOO°) of linoleate oxidize the semolina carotenoid pigments, thus leading to carotenoid loss and discoloration of the end product.
Borrelli, G.M.; Trono, D. Molecular Approaches to Genetically Improve the Accumulation of Health-Promoting Secondary Metabolites in Staple Crops—A Case Study: The Lipoxygenase-B1 Genes and Regulation of the Carotenoid Content in Pasta Products. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1177.
Link:


Nenhum comentário:
Postar um comentário